Where Does Wind Power Come From?
Inspire Clean Energy
Mar 19, 2020
5 min read
category: Clean Energy 101
Don't worry about climate change— do something about it.
Our clean energy plans are the easiest way to reduce your home's carbon footprint.
Switch to clean energyWhere does wind power come from?
Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, people around the world have become increasingly reliant on fossil fuels to power everything from lamps to motor vehicles. Over the past thirty years, though, we've been going through these fossil fuels at an increasingly faster rate — and eventually we're going to run out. Adding to the concerns surrounding our reliance on a such a limited resource, the burning of fossil fuels is also taking a serious toll on our environment as a result of carbon emissions. This has led to the development of and increased the demand for newer, cleaner sources of renewable energy. And one of the leading clean energy technologies comes in the form of wind power.
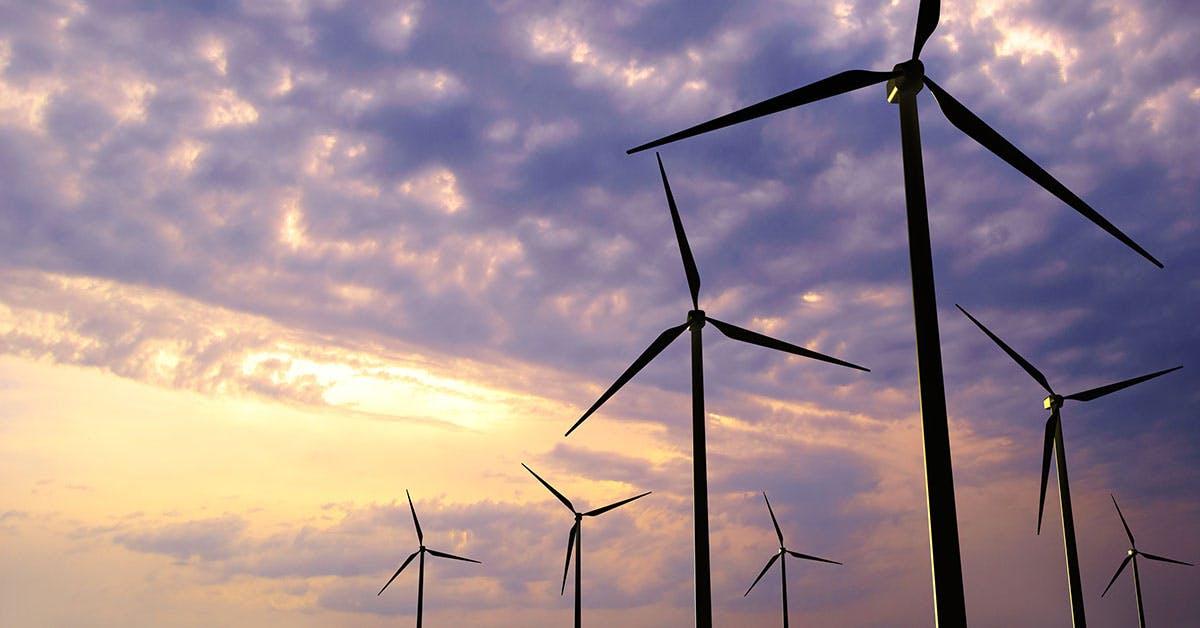
The idea of using the wind as a power source isn't anything new. After all, wind has powered sailing ships for well over 7,000 years, and windmills have long been used to process grain. Today, advancements in wind turbine technology have allowed us to harness the wind's power with greater efficiency and reliability. Depending on where you live, you may have even driven past a wind farm. In fact, according to the American Wind Energy Association, as of 2020, there are over 60,000 wind turbines generating electricity in 41 different states across the US, making it one of the largest and most impactful renewable energy sources in the country1.
So, what's going on inside a wind turbine?
A wind turbine works much like a pinwheel — when wind blows into it, it spins. But with wind turbines, this spinning is turned into electricity. More specifically, the process of turning wind into electricity starts with the circular arrangement of large rotor blades, which come together to form the turbine or "pinwheel" shape.
Turbine blades are designed to have just the right curvature so they can capture as much wind as possible. Then, the wind turbines are able to capture the kinetic energy as the wind pushes into them, spinning the blades.
The spinning of these blades then spins gears inside of a gearbox. This gearbox is located inside the body of the turbine, which is also known as the nacelle, which the blades are attached to. The drive shaft's rotation, powered directly by the blades, is slow - around 16 RPM (revolutions per minute). But as the gears wind up, they convert this motion into a much faster rotation of 1,600 RPM. This then powers an electrical generator, which transfers usable power directly to the electrical grid before it finally makes its way to your home.
Wind farms: On land and at sea
A wind farm is simply a grouping of a number of wind turbines set up near one another, designed to harness enough electricity for utility applications.
There are two main types of wind farms: onshore wind farms and offshore wind farms.
Onshore wind farms are typically clustered in particularly windy areas of land. One example is California's San Gorgonio Pass wind farm. This area was perfect for a wind farm because it's one of the windiest spots in the state, making it capable of generating power consistently throughout the year. There are other wind farms just like this scattered across the United States.
Offshore wind farms take advantage of the higher, more consistent wind speeds that are found at sea. Offshore turbines can harness quite a bit more power than wind farms located on land, but the logistics of constructing them are more challenging. Still, as the technology continues to be developed, it's becoming easier to make use of high-output offshore wind farms.
The future of wind power
As a technology, wind power is still in its infancy — but it's growing quickly.
This powerful renewable resource is one of the best candidates for a viable alternative to fossil fuels. For years, wind power has been one of the fastest growing clean energy technologies in the United States.
Offshore wind energy is a particularly promising new frontier. The winds at sea are stronger and more consistent than those on land, making offshore wind farms an appealing resource for clean, efficient energy generation. The obstacle has been a matter of logistics. Building wind farms located offshore is an expensive and challenging undertaking, as is transmitting electricity efficiently from the wind farm to the power grid.
Engineers and researchers have long been working to solve these problems, and in the future, the power of wind is expected to grow even more. Simple yet remarkably effective, wind turbines will continue to be a powerful and plentiful source of clean energy in the coming decades.
You can help!
Switching your home to clean energy is easy and can help you have a huge impact on climate change every day. Reduce your home’s net-carbon emissions in minutes by switching to 100% renewable energy for your home from sources like wind.
Learn more about the clean energy programs offered by Inspire. You can also read Inspire Clean Energy reviews to see how we've helped people like you make the switch!
- awea.org/wind-101/basics-of-wind-energy/wind-facts-at-a-glance↩
Don't worry about climate change— do something about it.
Our clean energy plans are the easiest way to reduce your home's carbon footprint.
Switch to clean energy
Inspire Clean Energy
We're on a mission to transform the way people access clean energy and accelerate a net-zero carbon future.
Learn more about Inspire →Explore more
Recent Posts
Top Articles